TelePulse: Enhancing the Teleoperation Experience through Biomechanical Simulation-Based Electrical Muscle Stimulation in Virtual Reality
CHI ’25
Title: TelePulse: Enhancing the Teleoperation Experience through Biomechanical Simulation-Based Electrical Muscle Stimulation in Virtual Reality
Authors: Hwang, S., Kang, S., Oh, J., Park, J., Shin, S., Luo, Y., DelPreto, J., Matusik, W., Rus, D., and Kim, S.
Conference: CHI ’25: ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
Awards: 🏆 Best Paper (Top 1%)
⚡ Project Overview
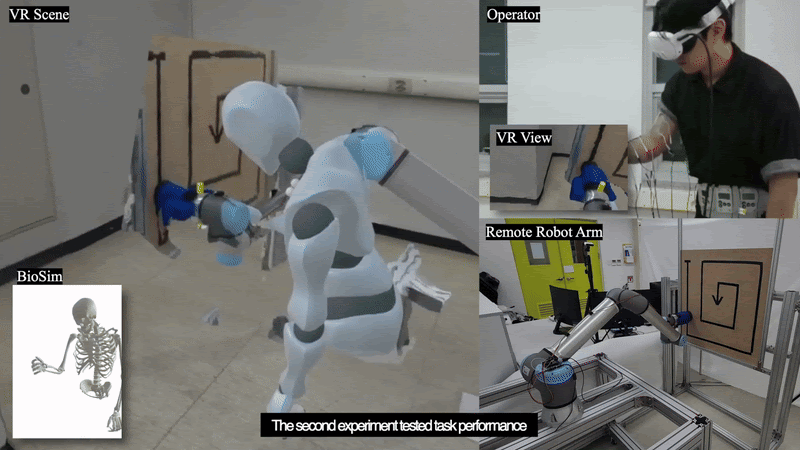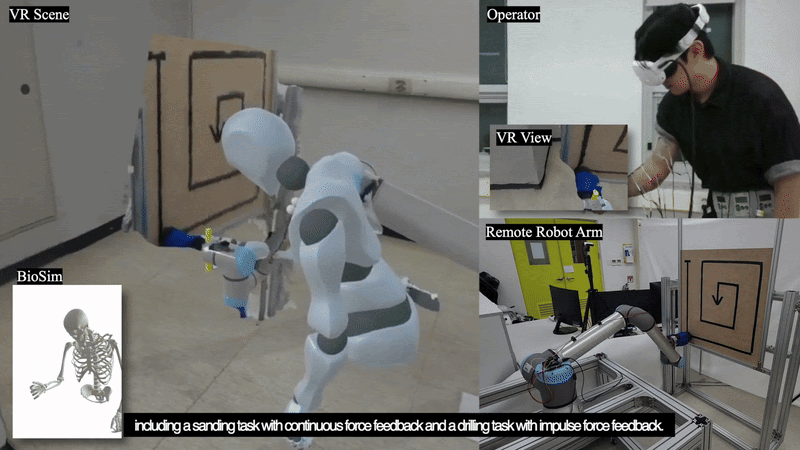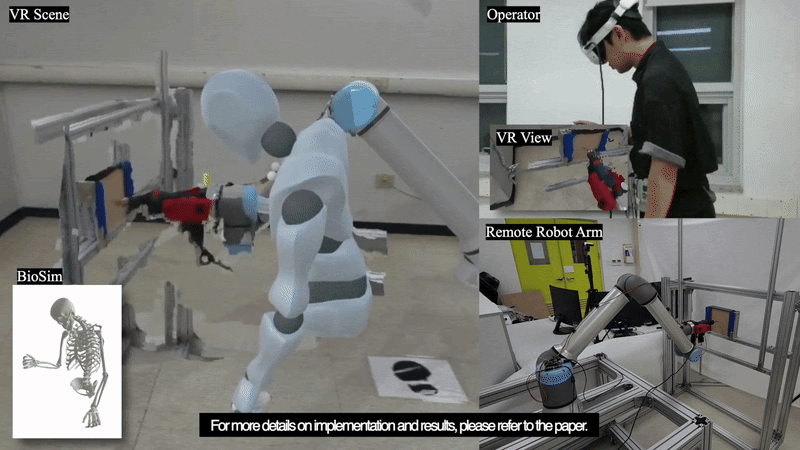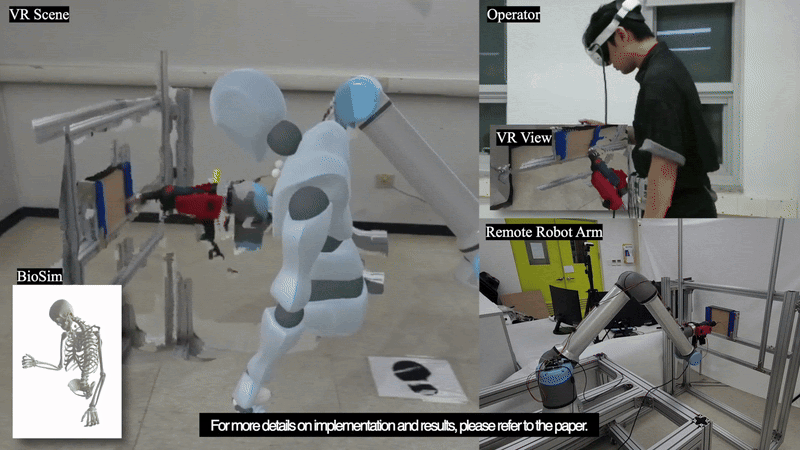
This paper introduces TelePulse, a system integrating biomechanical simulation with electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) to provide precise haptic feedback for robot teleoperation tasks in virtual reality (VR). TelePulse has two components: a physical simulation part that calculates joint torques based on real-time force data from remote manipulators, and an electrical stimulation part that converts these torques into muscle stimulation. Two experiments were conducted to evaluate the system. The first experiment assessed the accuracy of EMS generated through biomechanical simulations by comparing it with electromyography (EMG) data during forcedirected tasks, while the second experiment evaluated the impact of TelePulse on teleoperation performance during sanding and drilling tasks. The results suggest that TelePulse provided more accurate stimulation across all arm muscles, thereby enhancing task performance and user experience in the teleoperation environment. In this paper, we discuss the effect of TelePulse on teleoperation, its limitations, and areas for future improvement.
🔗 Link
Click here for more information about this project.
